Bias and Variance are terms that are frequently used in Machine Learning that hold special importance in understanding the application and performance of
ML models on datasets. However, many aspiring Machine Learning Engineers or Data Scientists have difficulty in properly understanding the concept and definitions
of these terms. Hence, there is always some confusion with regards to the usage of Bias and Variance in Machine Learning.
When building a Machine Learning Classification model, the dataset is usually divided into two or more subsections: most notably training, development, and testing set.
Training and Development sets are used to fit and adjust the parameters of the model that can most accurately predict the target variable while testing sets are used to
test our model on real world data to see how they perform. We will use our understanding of these datasets to explore the concept of bias and variance.
When training a model on the training dataset, sometimes the model may be too specific to that particular dataset. In other words, the values of the parameters of the
model may be too specific on the training set, allowing the model to predict the target variables of the training set perfectly.
However, when the model is used to predict variables on another dataset, such as the test set, because the model parameters have been adjusted and fit so specifically
to the training set, it might not be able to generalize and accurately predict the target variables of the test set, i.e. the model has overfitted (fit too well) on the training set.
Overfitting can be recognized by looking at the error of the model on training and test sets- the training set error is substantially smaller than the test set error. When this happens, the model is said to have high variance, i.e. the model performance on different datasets varies significantly.
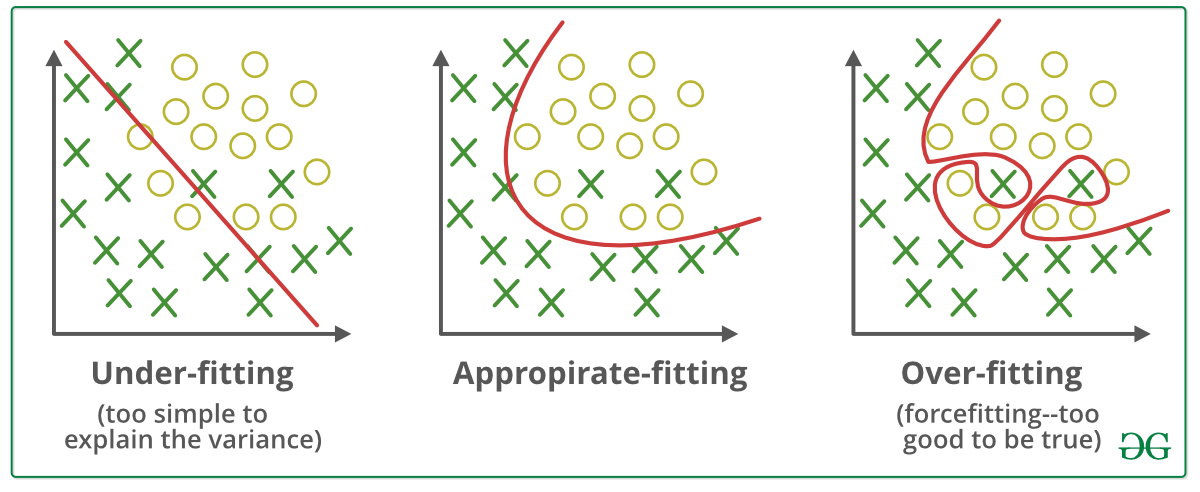
In contrast, when a model’s parameters do not adjust accurately and specifically even to the training dataset, the model is said to have high bias.
When working with a small training dataset with less number of features or records, machine learning models will have difficulty in predicting the target variables due to
the lack of data, i.e. the model will not be able to adjust its parameters accordingly to fit the dataset and predict the target variable.
This is known as underfitting and will lead to high error in both the training and the testing dataset.
| |
High Bias |
High Variance |
High Bias and Variance |
Low Bias and Variance |
| Train Set Error |
20% |
1% |
20% |
1% |
| Test/ Dev Set Error |
20% |
15% |
35% |
1% |
How to deal with high bias and variance?
High Variance is usually caused when the model is not able to generalize its parameter values to other datasets. Hence, it is important to regulate the parameters to get rid of overfitting. The process of regulating is also known as regularization. Regularization helps prevent overfitting by adjusting the values of the parameters, usually to lower absolute values. Another method of preventing overfitting is by adding more data to allow our model to ignore noisy inputs.
High Bias is usually caused due to the over-simplicity of a model. Hence, we can easily solve this issue by using a more complicated model that can capture all the important features of our dataset.
Auras Khanal